When it comes to hosting applications, scaling is crucial. Horizontal and vertical scaling are the main strategies.
Choosing the right scaling method is essential for application performance and growth. Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers to handle the load. In contrast, vertical scaling means adding more power to an existing server. Understanding the differences can help you make informed decisions for your business. This guide will explore the key aspects of horizontal and vertical scaling, helping you determine which is best for your needs. You can ensure your applications run smoothly and efficiently with the right approach. For reliable hosting solutions that support both scaling options, consider Liquid Web for its high-performance and customizable services.
Credit: www.cloudzero.com
Introduction To Scaling In Application Hosting
Scaling is essential for hosting applications. It enhances performance, ensuring seamless user experiences. There are two primary types: horizontal and vertical scaling. Understanding these can help optimize your application’s performance efficiently.
Understanding Scaling
Scaling involves adjusting resources to meet application demands. This can be crucial for handling traffic spikes, maintaining performance, and ensuring uptime.
Horizontal Scaling: Adding more servers to distribute the load.
Vertical Scaling: Increasing the capacity of a single server.
Each method has its benefits and challenges. Knowing when to use each can save costs and improve reliability.
Importance Of Scaling For Application Performance
Proper scaling directly impacts application performance. It ensures your application remains fast and responsive under heavy loads. This is vital for user satisfaction and retention.
Liquid Web offers scalable solutions:
Hosting Type | Starting Price | Scalability |
|---|---|---|
Cloud Hosting | $149/month | Highly scalable |
VPS Hosting | $59/month | Moderately scalable |
Dedicated Servers | $169/month | Limited scalability |
Managed WordPress Hosting | $19/month | Scalable |
Choosing the right hosting type depends on your application’s needs and growth projections.

Credit: www.youtube.com
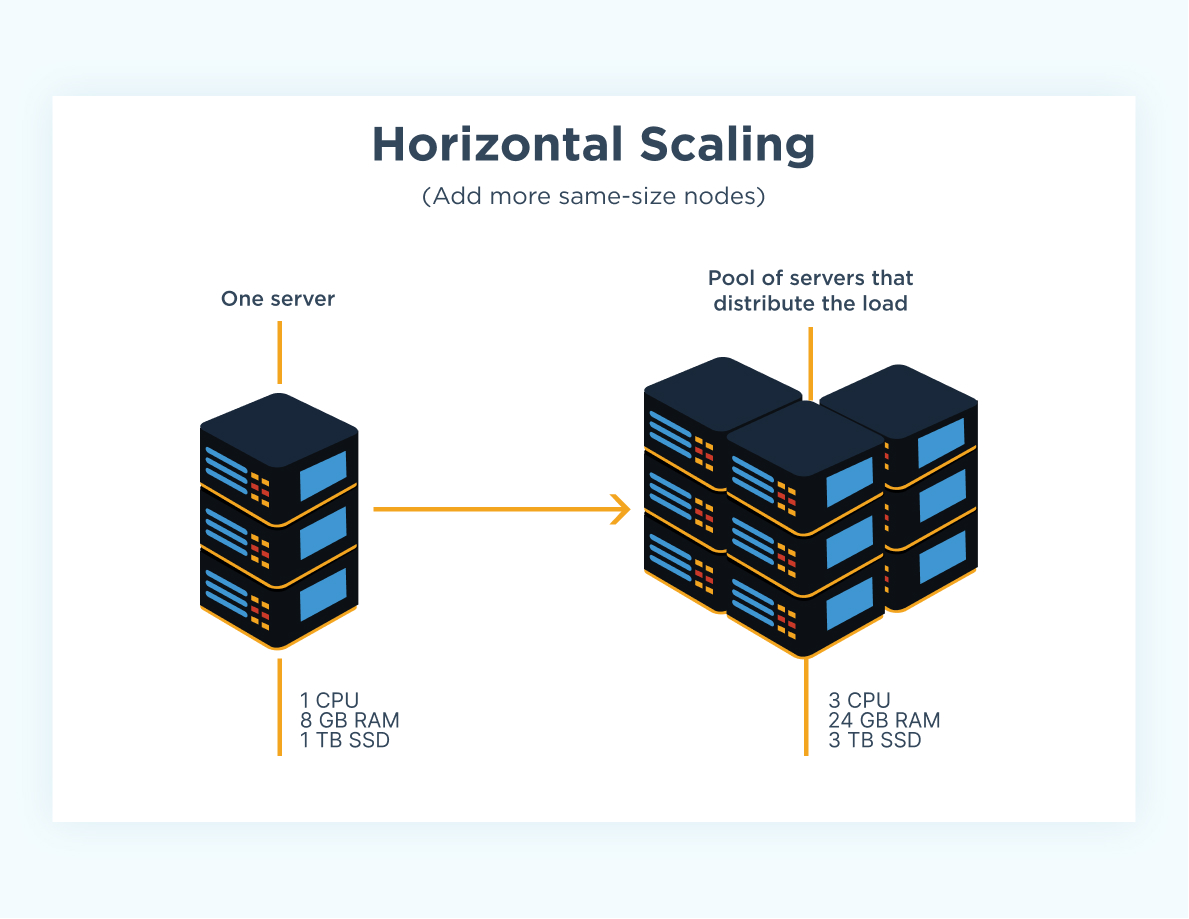
What Is Horizontal Scaling?
Horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out, involves adding more servers to your existing pool of resources. This method helps manage increased traffic and workload by distributing tasks across multiple machines. Horizontal scaling is ideal for businesses experiencing rapid growth or fluctuating demand.
Definition And Concept
Horizontal scaling refers to increasing the number of servers or nodes in a system. Instead of upgrading the capacity of a single server, you add more servers to share the load. This approach enhances performance, reliability, and availability.
Horizontal Scaling | Vertical Scaling |
|---|---|
Adds more servers | Upgrade the existing server |
Distributes tasks | Increases capacity |
Improves redundancy | Single point of failure |
How Horizontal Scaling Works
Horizontal scaling works by adding more machines to handle increased traffic. Each server operates independently but contributes to the overall workload. A load balancer distributes incoming requests across all servers, ensuring efficient resource use.
Identify the need for additional resources.
Add new servers to the network.
Configure the load balancer to distribute tasks.
Monitor performance and adjust as needed.
Benefits Of Horizontal Scaling
Enhanced Reliability: Multiple servers reduce the risk of downtime.
Improved Performance: Distributes traffic, minimizing load on individual servers.
Scalability: Easily add more servers as demand grows.
Cost-Effective: Often cheaper than upgrading a single server’s hardware.
Liquid Web offers tailored hosting solutions for businesses needing high performance and reliability. Their managed hosting services include fully managed VPS, dedicated servers, and cloud hosting. With 24/7 customer support and enhanced security, Liquid Web ensures your business stays online and secure.
Explore more about Liquid Web’s offerings at Liquid Web Hosting Services.
What Is Vertical Scaling?
Vertical scaling, often referred to as scaling up, is a common method for increasing the capacity of your application hosting environment. This approach involves adding more power to an existing server, rather than adding more servers to the network.
Definition And Concept
Vertical scaling means increasing the power of a single server. This can be achieved by adding more CPU, RAM, or storage resources.
Imagine a ladder. Scaling vertically is like climbing higher on the same ladder. You enhance the capabilities of your current setup without changing its structure.
How Vertical Scaling Works
Vertical scaling involves upgrading your server’s hardware. For example, increase the RAM from 16GB to 32GB or upgrade the CPU to a faster model.
This method is straightforward. Your existing applications and data remain on the same machine, making the process simpler and quicker.
Here is a table to illustrate the process:
Resource | Before Scaling | After Scaling |
|---|---|---|
CPU | 4 Cores | 8 Cores |
RAM | 16GB | 32GB |
Storage | 1TB | 2TB |
Benefits Of Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling offers several advantages:
Simplicity: Upgrading hardware is usually easier than adding new servers.
Cost-Effective: It can be more affordable initially as it doesn’t require additional infrastructure.
Less Downtime: Often results in less downtime compared to horizontal scaling.
Improved Performance: Enhanced resources lead to better application performance.
Vertical scaling is an excellent choice for small to medium-sized applications. It ensures your applications run smoothly without needing a complex setup.
VerticalVertical scaling is a straightforward way to enhance performance for managed hosting services like Liquid Web for managed hosting services like Liquid Web. Their high-performance servers and expert support make scaling up a breeze.
Key Differences Between Horizontal And Vertical Scaling
Understanding the key differences between horizontal and vertical scaling is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their application hosting. Each method offers unique benefits and challenges that can impact performance, cost, and implementation.
Scalability And Flexibility
Horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out, involves adding more machines to your pool of resources. This method offers greater flexibility as you can add more servers as needed.
On the other hand, vertical scaling, or scaling up, involves adding more power (CPU, RAM) to an existing machine. While this can be simpler to implement, it has a limit based on the capacity of a single server.
Cost Implications
The cost implications of each scaling method can vary significantly. Horizontal scaling often involves higher initial setup costs due to the need for additional hardware and potentially more complex configurations. However, it can be more cost-effective in the long run as it allows for incremental growth.
Vertical scaling may have lower initial costs, but the expenses can increase rapidly as the need for more powerful hardware grows. Additionally, there’s a ceiling to how much you can scale vertically, which can limit long-term growth.
Performance And Reliability
Horizontal scaling generally offers better performance and reliability. Distributing the load across multiple servers ensures your application remains responsive even during peak times.
In contrast, vertical scaling can result in a single point of failure. If your server goes down, your entire application can be affected, making it less reliable in critical situations.
Implementation Complexity
Implementing horizontal scaling can be more complex. It often requires changes to the application architecture to ensure that it can run on multiple servers. Load balancers and distributed databases are also commonly needed.
Vertical scaling is generally simpler to implement. You upgrade the existing server without needing to change the application architecture. This makes it an attractive option for businesses looking for straightforward solutions.
Pros And Cons Of Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out, involves adding more servers to your existing setup. This approach can significantly improve the performance and reliability of your application hosting. However, like any other solution, it has advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages Of Horizontal Scaling
Improved Performance: Adding more servers can distribute the load, enhancing the overall performance.
High Availability: With multiple servers, the failure of one server does not impact the entire system.
Scalability: It’s easier to scale horizontally by adding more servers as your needs grow.
Cost-Effective: Often more affordable than vertical scaling, which requires more powerful (and expensive) servers.
Flexibility: Allows for the use of commodity hardware, making it easier to manage and replace servers.
Disadvantages Of Horizontal Scaling
Complexity: Managing a larger number of servers can be challenging and requires advanced skills.
Network Overhead: Increased communication between servers can lead to network latency issues.
Consistency: Ensuring data consistency across multiple servers can be complex and may require sophisticated solutions.
Initial Setup: Requires a significant initial setup and configuration, which can be time-consuming.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of multiple servers can be resource-intensive.
Pros And Cons Of Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, also known as scaling up, involves adding more power to an existing server. This can include adding more CPU, RAM, or storage. It’s a popular method for businesses that require increased performance from their hosting solutions.
Advantages Of Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling has several benefits, making it an attractive option for many businesses.
Simplicity: Easy to implement without changing your existing code or architecture.
Cost-Effective: Initially cheaper than horizontal scaling as it doesn’t require additional hardware.
Management: Easier to manage with fewer servers to maintain.
Performance: Can provide immediate performance improvements with upgrades.
Disadvantages Of Vertical Scaling
Despite its benefits, vertical scaling also comes with some limitations.
Limits: Physical limits on how much you can scale a single server.
Downtime: Downtime may be required to upgrade the server hardware.
Cost: Long-term costs can be high as upgrades become more expensive.
Single Point of Failure: All hosted applications are affected if the server fails.
When considering vertical scaling, weigh these pros and cons carefully. This ensures you choose the best approach for your business needs.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xpDnVSmNFX0
Choosing The Right Scaling Strategy
The ideal scaling strategy is crucial for your application’s performance and cost-efficiency. The two main types are horizontal scaling and vertical scaling. Each has its advantages and is suitable for different use cases. Below, we’ll explore the factors to consider and specific scenarios for both strategies.
Factors To Consider
When deciding between horizontal and vertical scaling, several factors come into play:
Application Architecture: Does your application support distributed computing?
Budget: What are your financial constraints?
Traffic Patterns: How predictable is your traffic?
Data Consistency: Do you need strong data consistency?
Downtime Tolerance: Can your application afford downtime?
Specific Use Cases For Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out, involves adding more servers to handle increased load. It is ideal for:
Web Applications: Websites with fluctuating traffic can benefit from multiple servers handling the load.
Microservices Architecture: Applications built with microservices can distribute services across several servers.
Cloud Environments: Cloud hosting solutions, like those offered by Liquid Web, make adding or removing servers easy.
Specific Use Cases For Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, also known as scaling up, involves adding more resources (CPU, RAM) to a single server. It suits:
Legacy Applications: Older applications that can’t easily distribute workloads.
Databases: Databases requiring high data consistency perform better with more powerful servers.
Single-Server Deployments: Small businesses with a single server can enhance performance by upgrading hardware.
Choosing the right scaling strategy is essential for maintaining application performance and reliability. Consider your specific use cases and requirements, whether you opt for horizontal or vertical scaling.

Credit: www.liquidweb.com
Frequently Asked Questions
When To Use Horizontal Vs Vertical Scaling?
Use horizontal scaling to add more servers for increased capacity. Opt for vertical scaling to upgrade existing server hardware.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Vertical Server Scaling?
Vertical server scaling is costly and has hardware limits. It risks downtime during upgrades. It’s less flexible than horizontal scaling.
Which Of The Following Is A Reason To Prefer Horizontal Scaling Over Vertical Scaling When Deploying Containers In A Cluster?
Horizontal scaling offers better load distribution and fault tolerance. It enhances application performance by adding more container instances.
Why Is Vertical Scaling Less Common In Cloud Environments?
Due to cost inefficiency and limited hardware upgrade options, vertical scaling is less common in cloud environments. Horizontal scaling offers better flexibility and performance.
Conclusion
Choosing between horizontal and vertical scaling depends on your application needs. Horizontal scaling adds more servers to handle traffic. Vertical scaling enhances a single server’s capacity. Both have advantages and limitations. Horizontal scaling offers better redundancy. Vertical scaling is easier to implement initially. Assess your growth projections and budget. For reliable and scalable hosting, consider Liquid Web. Their managed solutions provide high performance and security. With 24/7 expert support, your site remains secure and fast. Explore their flexible plans to meet your unique needs. Make the right choice for your business today.
